Our power to weight ratio calculator is ideal if you are wondering how to compare the performance of several cars. In the following text, find out how to calculate the power to weight ratio and why it is an important indicator of a vehicle’s performance.
Power to Weight Ratio Calculator
More Calculators
What is the Power to Weight Ratio?
The power-to-weight ratio (PWR) is an important indicator for evaluating the performance and efficiency of vehicles, engines, and athletes. It measures how much power is generated per unit of weight. The higher the power to weight ratio, the better the performance, whether cars, bikes, or personal fitness. This ratio is crucial for enthusiasts and professionals who want to maximize speed and agility.
What is the power-to-weight ratio and how useful is it?
Different vehicles have different performance and weigh different amounts. For example, a Ford F-Series pickup has a peak power of 290 hp (216 kW) and weighs 4,069 lb (1,846 kg), while a Ford Fiesta has 89 hp (66 kW) and weighs 2,546 lb (1,155 kg). How can we fairly compare their performance based on these figures?
What we need is a metric that does not depend on the size of the vehicle. The solution is to divide the power of the vehicle by its weight (or mass) to get the power-to-weight ratio. But what does that mean exactly? It is a measure of how much power the vehicle can generate per unit of weight. The two most common units for power-to-weight ratio are horsepower per pound (hp/lb) and kilowatts per kilogram (kW/kg). If a car has a higher horsepower per pound than another vehicle, it can accelerate that pound of weight faster. An example of a fast-accelerating vehicle is a motorcycle, which may have average power. However, because it is very light, its power-to-weight ratio is much greater than that of a typical car.
It should be noted that the term “weight” used in this article refers to mass. For example, to calculate the power-to-weight ratio of the moon buggy, you would use its mass and not its weight measured on the moon, which is one-sixth of the weight measured on Earth.
How do you calculate power to weight ratio?
- Look up the power of the vehicle. You will find this value in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or you can look it up online.
- Determine the unladen weight of the vehicle. You can also find this information either in the owner’s manual or in an online source. The unladen weight is the weight of the vehicle without the driver, passengers, and luggage.
- Calculating the power-to-weight ratio (PWR) is straightforward. The power-to-weight ratio is a measure of performance and is calculated by dividing the power output of an object (such as a vehicle or engine) by its weight. The formula for calculating PWR is:
PWR = Power/Weight
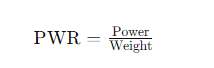
Apply the Formula:
- Divide the power output by the weight to obtain the power-to-weight ratio.
- The result will depend on the units used. Common expressions include:
- Watts per kilogram (W/kg): For power in watts and weight in kilograms.
- Kilowatts per kilogram (kW/kg): For power in kilowatts and weight in kilograms.
- Horsepower per pound (hp/lb): For power in mechanical horsepower and weight in pounds.
Example Calculation:

So, the power-to-weight ratio is approximately 0.1491 kW/kg.
Example of Power-to-weight ratio
| Example | Power (W or hp) | Weight (kg or lb) | Power-to-Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Professional Cyclist | 400 W | 70 kg | 5.71 W/kg |
| Sports Car | 500 hp | 1500 kg | 0.33 hp/kg (approx. 246 W/kg) |
| Motorcycle | 200 hp | 200 kg | 1.00 hp/kg (approx. 745 W/kg) |
| Formula 1 Car | 1000 hp | 750 kg | 1.33 hp/kg (approx. 993 W/kg) |
| Sedan | 200 hp | 1800 kg | 0.11 hp/kg (approx. 82 W/kg) |
| Amateur Cyclist | 250 W | 80 kg | 3.13 W/kg |
| SUV | 300 hp | 2200 kg | 0.14 hp/kg (approx. 105 W/kg) |
| Jet Fighter (F-16) | 29,000 hp | 12,000 kg | 2.42 hp/kg (approx. 1805 W/kg) |
| Weightlifter (Snatch Lift) | 1000 W | 90 kg | 11.11 W/kg |
| Compact Car | 150 hp | 1200 kg | 0.125 hp/kg (approx. 93 W/kg) |
Why Power-to-Weight Ratio Matters
A higher power-to-weight ratio generally means better performance, especially in vehicles such as cars, motorcycles, or airplanes, as more power is available per unit of weight, resulting in faster acceleration and better handling. In sports and fitness, a higher PWR can mean more speed and agility for athletes.
What is the power-to-weight ratio of an F1 car?
1297 hp/t | 967 W/kg | 0.588 hp/lb. F1 cars have a minimum weight of 798 kg (1,759 lbs) and about 772 kW (1035 hp), which corresponds to a power-to-weight ratio of 1297 hp/t.
What is a good power to weight ratio in kg?
A good power-to-weight ratio in kilograms for average vehicles is generally around 0.1 kW/kg (100 W/kg), while high-performance sports cars typically have values of 0.2 kW/kg (200 W/kg) or more. In competitive sports such as cycling, elite athletes may aim for a power-to-weight ratio of 6 to 7 W/kg.
Is 200 watts good cycling?
Yes, 200 watts is a solid power output for cycling, especially for recreational or amateur cyclists. It indicates good fitness and can be challenging to maintain for extended periods. However, what qualifies as “good” can vary depending on factors like experience level, body weight, and cycling goals.

